Migrating data from SQL Server to MariaDB
This guide walks you through migrating data from SQL Server to MariaDB in a few simple steps using ESF Database Migration Toolkit. Simplify complex migration tasks and save valuable time with our streamlined approach.
SQL Server vs. MariaDB:
- SQL Server is a robust relational database management system developed by Microsoft, designed for a wide range of data management applications. It supports a variety of transaction processing, business intelligence, and analytics applications in corporate IT environments. Known for its high performance, scalability, and security features, SQL Server offers comprehensive tools for database creation, management, and maintenance, making it a preferred choice for both small-scale applications and large enterprise systems. Its integration with other Microsoft products and services further enhances its versatility and ease of use.
- MariaDB is a powerful open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that originated as a fork of MySQL. It was developed by the original creators of MySQL in response to concerns over its acquisition by Oracle Corporation. MariaDB retains compatibility with MySQL while offering additional features, improved performance, and enhanced security. It is widely used in various applications ranging from small-scale web databases to large-scale enterprise systems, thanks to its flexibility, scalability, and active community support.
Prerequisite:
Software Required:
DMToolkit_x64.zip
(63.6 MiB)64-bit Windows application for ESF Database Migration Toolkit 12.2.08 (2025-07-11).
(md5: e93a0ef57622bfd8ee77d6aa6e38c13b)DMToolkit_win32.zip
(58.8 MiB)32-bit Windows application for ESF Database Migration Toolkit 12.2.08 (2025-07-11).
(md5: bd34cb7f73c88c6d0c7a44069ad756d6)System Supported:
- Windows 7 or higher.
- SQL Server 6.5 or higher.
- MariaDB 5.1 or higher.
Step by Step Wizard:
-
Configure Microsoft SQL Server Data Source
- In the "Choose a Data Source" dialog:
- Select "Microsoft SQL Server"
- Server connection details:
- Enter host name (include instance if needed): e.g.,
localhost\sqlexpress - For TCP/IP connections:
- Port number:
0(default, uses named pipes) - Provide username (e.g.,
sa) and password
- Port number:
- Enter host name (include instance if needed): e.g.,
- Authentication method:
- Check Windows Authentication checkbox for integrated security
- Database configuration:
- Click Refresh Database to list databases
- Select existing database or enter new database name
- New databases are automatically created during migration
- Schema configuration:
- Click Refresh Schema to list schemas
- Select existing schema or enter new schema name
- New schemas are automatically created during migration
- Default:
dbo(if left empty)
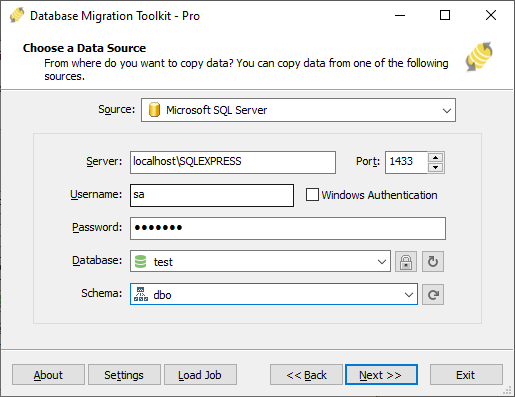
Fig. 1: Microsoft SQL Server data source configuration - In the "Choose a Data Source" dialog:
-
Configure MariaDB Destination
- In the "Choose a Destination" dialog:
- Select "MariaDB"
- Enter connection details:
- Server name:
localhost(default) - Port:
3306(default) - Username
- Password
- Server name:
- Optional settings:
- Select MariaDB Storage Engine
-
Choose character set (e.g.,
UTF-8)
- Database configuration:
- Click the Refresh button to list available databases
- Select existing database OR enter new database name
- Note: Non-existent databases will be automatically created during migration
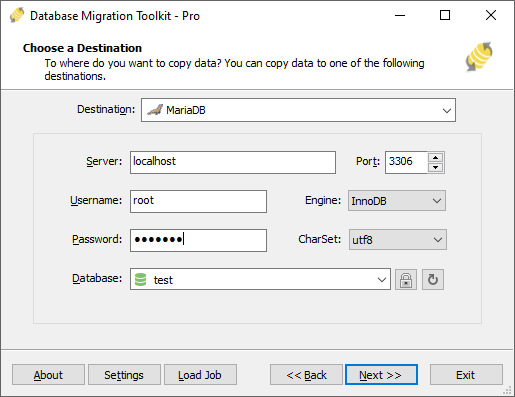
Fig. 2: MariaDB destination configuration - In the "Choose a Destination" dialog:
-
In "Select Source Table(s) & View(s)" Dialog
-
Select migration objects: Choose tables or views to include in the migration.
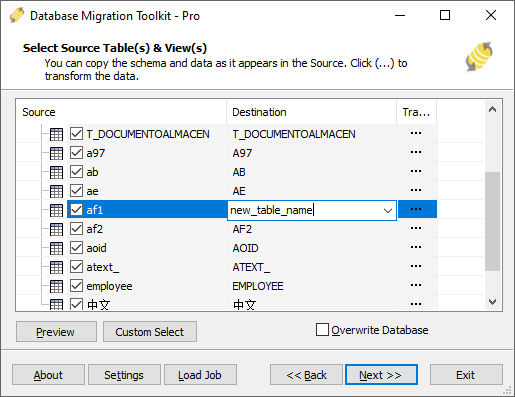
Fig. 3: Select tables and views -
Modify table structure: Click the ellipsis (...) button to access table options and schema adjustments.
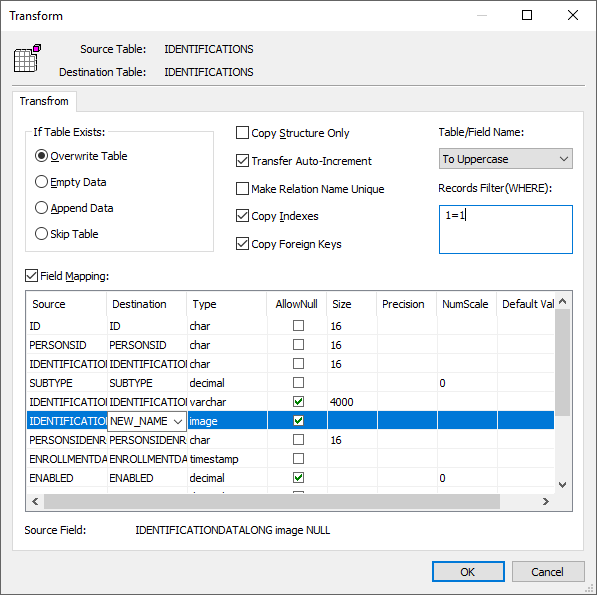
Fig. 4: Do transform -
Configure field mapping: In the Field Mapping options:
- Customize destination fields (name, data type, default value, comments)
- Select data transfer method:
- Overwrite Table (replace existing data)
- Empty Data (truncate before insert)
- Append Data (add to existing data)
- Skip Table (exclude from transfer)
- Apply data filters before transfer
-
Select migration objects: Choose tables or views to include in the migration.
-
Execution Dialog
-
Start migration: Click "Submit" to initiate automated data transfer from SQL Server to MariaDB.
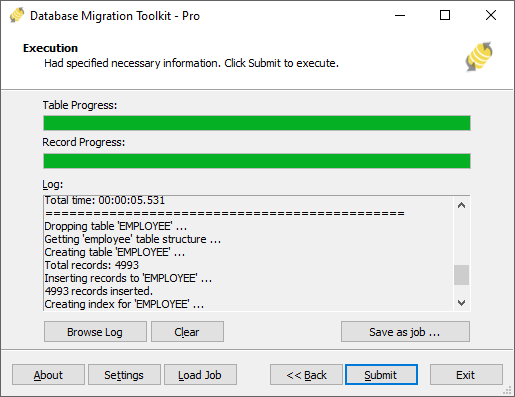
Fig. 5: Execute migration - Monitor progress: Click "Browse Log" for real-time migration tracking, including issue resolution details.
-
Save configuration: Click "Save as job" to store settings for:
- Quick reloads of migration jobs
- Command-line execution (use:
dmtc.exe --helpfor parameter options)
-
Start migration: Click "Submit" to initiate automated data transfer from SQL Server to MariaDB.
-
Finished!
After migration completes, the toolkit generates a comprehensive report for verifying migration accuracy. You can monitor progress as the automated process runs efficiently. For any questions or feedback, contact us – our team is ready to assist.